Rock Failure Theories in Rock Mechanics
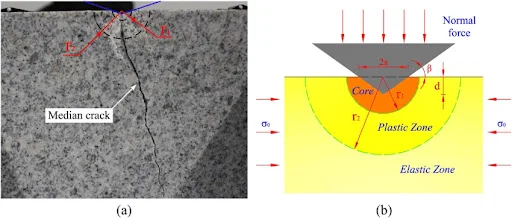
Illustration of rock failure mechanisms under stress
Rock failure occurs due to various stress conditions and is explained by several established theories in rock mechanics and geotechnical engineering. These theories help predict failure in slopes, tunnels, foundations, mining, and other rock engineering projects.
1. Mohr-Coulomb Theory
The Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion is the most widely used for rocks and soils. It assumes failure occurs when shear stress exceeds shear strength, which depends on cohesive strength (c) and internal friction angle (φ).
Key equation (shear strength τ):
τ = c + σ tan φ
Where σ is normal stress on the failure plane.
In principal stress terms:
σ₁ - σ₃ = (σ₁ + σ₃) sin φ + 2c cos φ
It provides a linear failure envelope in Mohr's circle representation.

Mohr-Coulomb failure envelope showing linear envelope tangent to Mohr circles at failure (principal stress space)

Classic Mohr circle representation with linear failure criterion
2. Griffith Theory
Developed by A.A. Griffith, this theory (linear elastic fracture mechanics) explains brittle failure due to pre-existing microcracks or flaws. Failure initiates when tensile stress at a crack tip exceeds the material's tensile strength.
It predicts crack propagation under tension or compression, with stress concentration at elliptical crack tips.
Key insight: Rocks fail at much lower stresses than theoretical strength due to flaws.
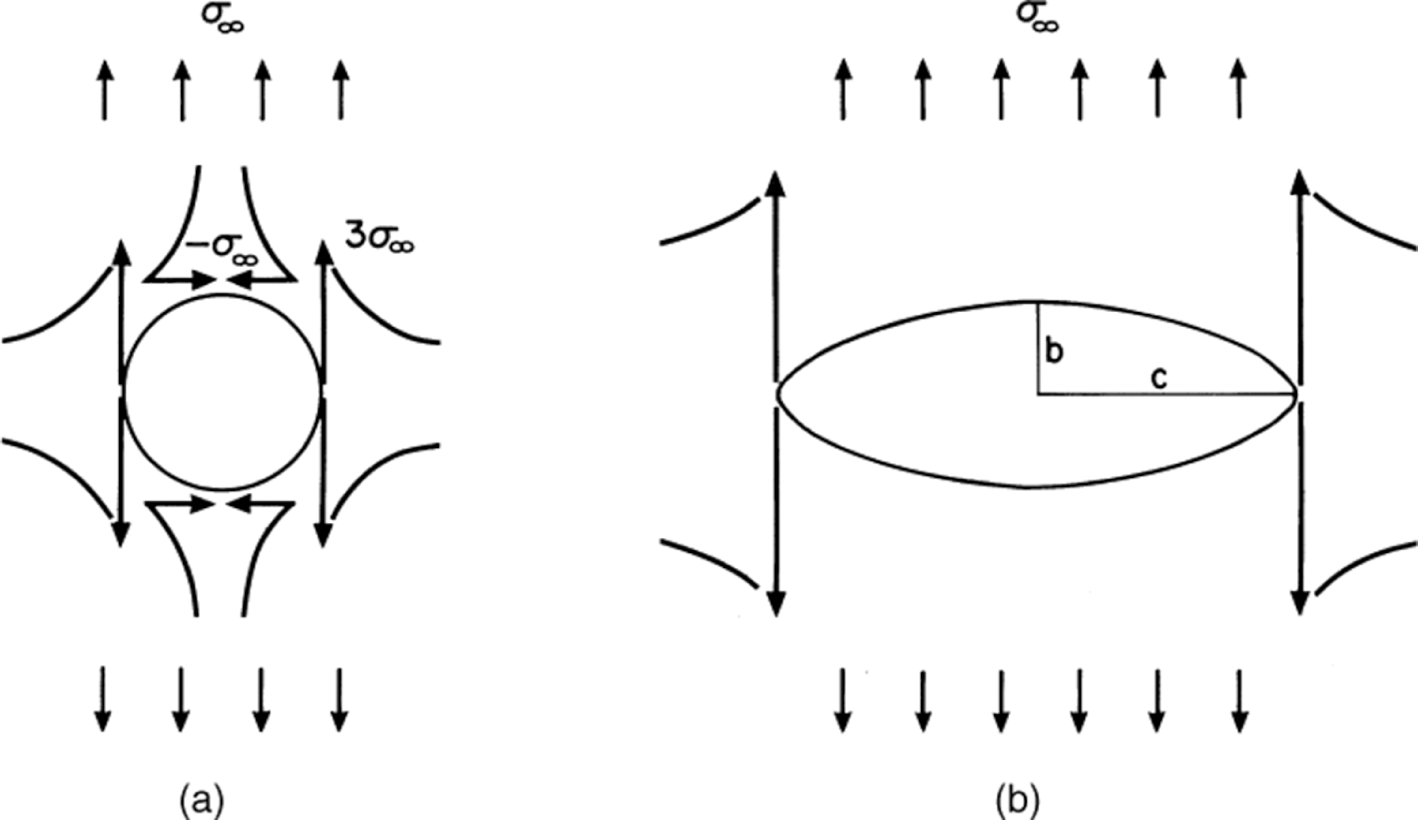
Griffith crack theory: Stress concentration around circular and elliptical flaws under uniaxial compression/tension

Illustration of Griffith's role of cracks in brittle fracture initiation
3. Hoek-Brown Failure Criterion
Proposed by Evert Hoek and E.T. Brown, this empirical nonlinear criterion is widely used for intact rock and rock masses. It accounts for rock mass quality via Geological Strength Index (GSI), disturbance, and parameters like mᵢ (intact rock constant).
Generalized form (intact rock, s=1, a=0.5):
σ₁ = σ₃ + σ_ci (mᵢ σ₃ / σ_ci + 1)^0.5
It better fits nonlinear behavior at high confinement and low tensile strength.

Hoek-Brown failure envelope showing transition from intact rock to rock mass strength with GSI

Comparison: Hoek-Brown nonlinear envelope vs. equivalent linear Mohr-Coulomb fit
4. Barton-Bandis Criterion
Developed by Nick Barton and S. Bandis for discontinuities (joints/fractures). It models shear strength of rough joints, incorporating joint roughness (JRC), joint wall compressive strength (JCS), and residual friction angle (φᵣ).
Key equation:
τ = σ_n tan(φᵣ + JRC × log₁₀(JCS / σ_n))
Useful for jointed rock masses where discontinuities control failure.
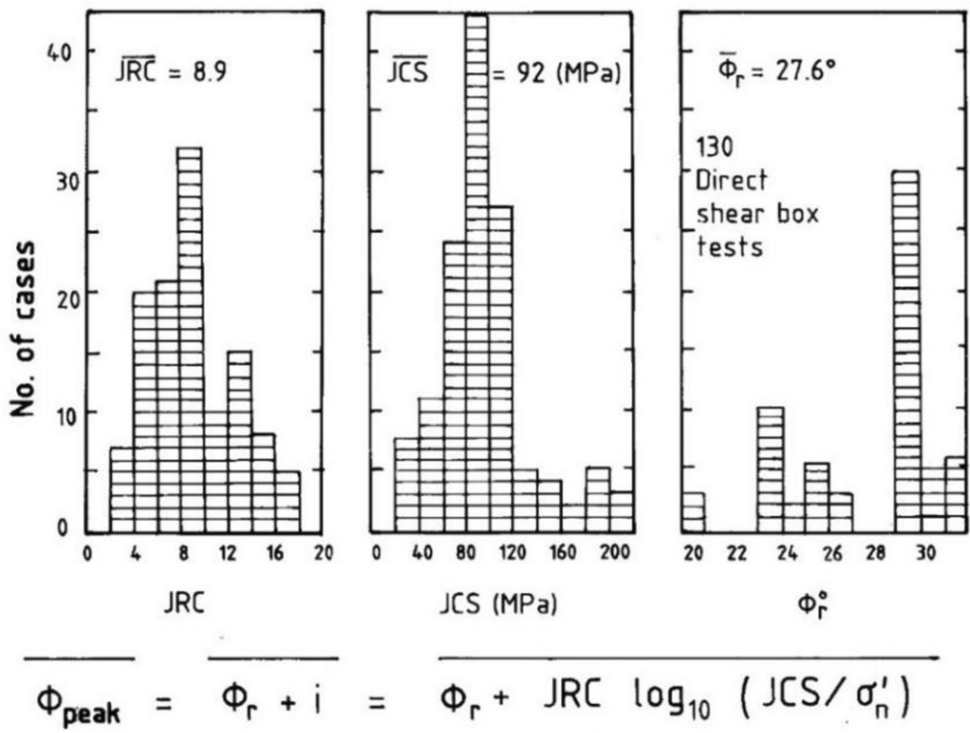
Barton-Bandis model: Distribution of JRC, JCS, and residual friction angle (φᵣ) from experimental data
5. Modified Cam-Clay Model
Primarily for soils but adapted for weak, weathered, or soft rocks. It models nonlinear elasto-plastic behavior, including volume changes (dilation/compaction) under stress.
It uses parameters like pre-consolidation pressure and critical state line, suitable for rocks showing ductile behavior.
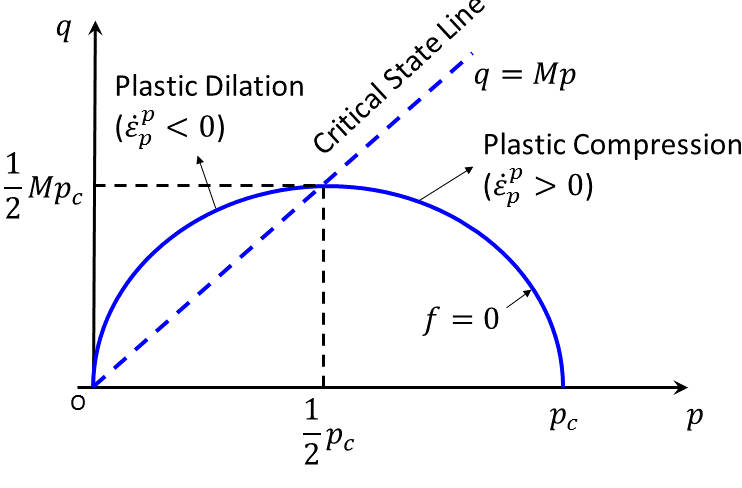
Modified Cam-Clay yield surface in p-q space showing critical state line and plastic zones
Comparison and Applications
- Mohr-Coulomb: Simple, linear, good for general use but overestimates tensile strength.
- Griffith: Best for brittle fracture initiation from flaws.
- Hoek-Brown: Preferred for rock masses in tunnels/mining (nonlinear, empirical).
- Barton-Bandis: Essential for joint shear in discontinuous rock.
- Modified Cam-Clay: For weak/deformable rocks with plastic flow.
Selection depends on rock type (intact vs. jointed), stress regime, and project needs (e.g., high confinement favors Hoek-Brown).
These theories form the foundation of rock engineering stability analysis. For precise applications, combine with field data, lab tests, and numerical modeling.

















0 Comments