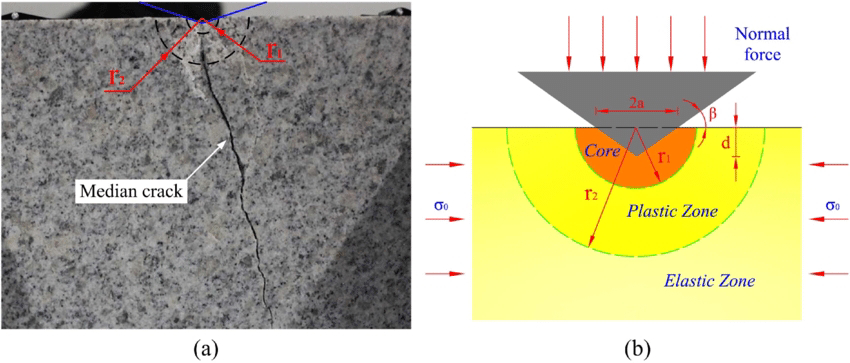
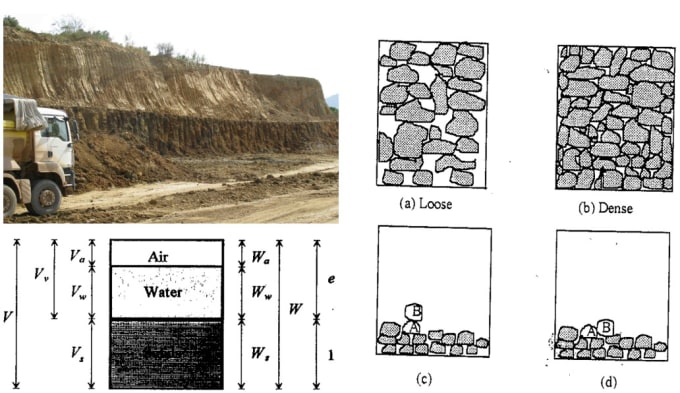
Subsidence

Subsidence: Geomechanics is a branch of geophysics and geotechnical engineering that focuses on the study of the mechanical behavior of rocks and soils. It combines principles from geology, physics, and engineering to understand how geological materials respond to external forces such as stress, temperature, and fluid pressure. Subsidence, in the context of geomechanics, refers to the gradual sinking or settling of the Earth's surface. It is often associated with the extraction of underground resources, such as oil, gas, or minerals, as well as with certain geological processes and human activities. There are several causes of subsidence: 1. Natural Subsidence: Natural processes, such as the compaction of sedimentary layers, dissolution of underground minerals (e.g., limestone), and erosion, can lead to subsidence over long periods of time. 2. Mining Subsidence: The extraction of underground resources, such as coal or minerals, can create voids in the subsurface. Over ...