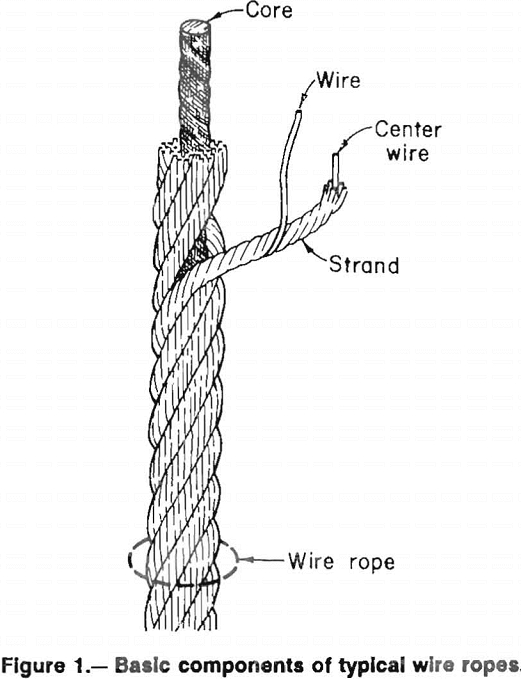
Mining Conveyors Overview
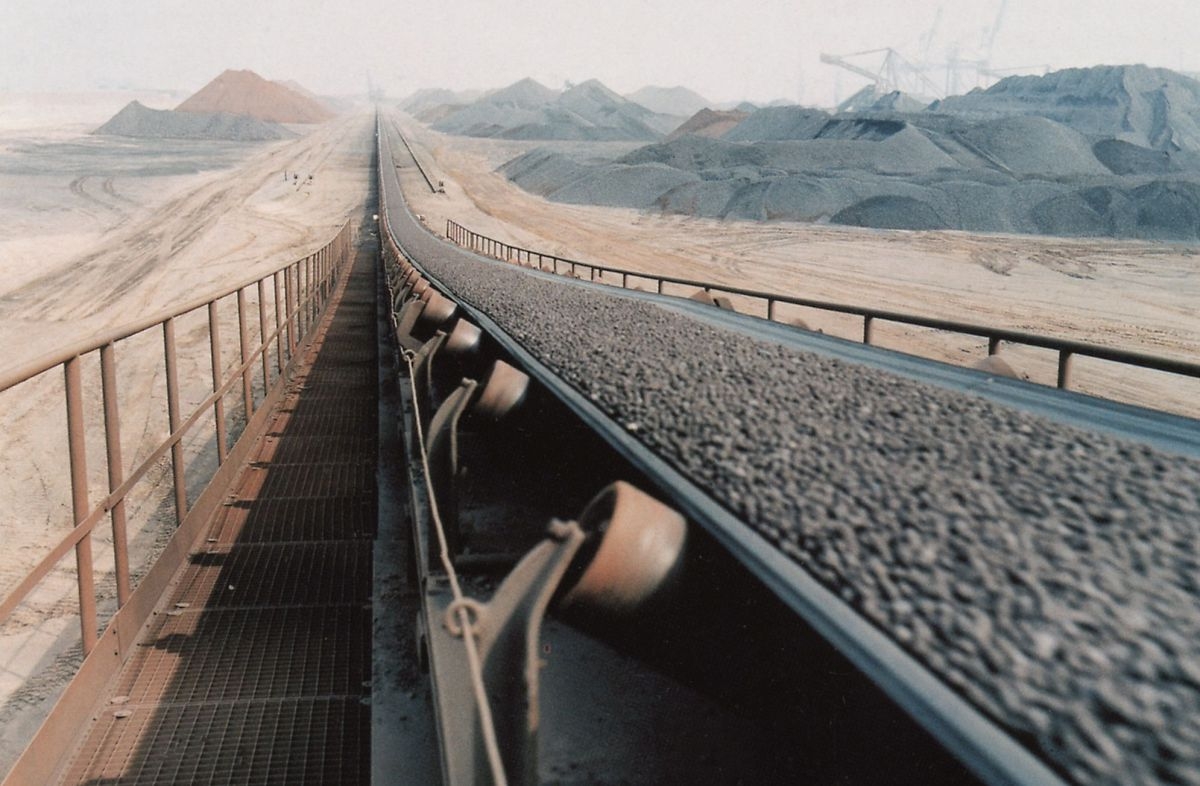

Mining Conveyors Overview: Conveyors play a crucial role in the mining industry by transporting bulk materials efficiently and safely. They are used to move various types of materials, such as coal, ore, rocks, and aggregates, over long distances, across different terrains, and between different processing stages within a mine site. Here are some key points about conveyors in mining: 1. Types of Conveyors: There are several types of conveyors used in mining operations, including belt conveyors, screw conveyors, vibrating conveyors, and bucket elevators. Belt conveyors are the most common and widely used, consisting of a continuous belt looped around pulleys and supported by idler rollers. 2. Material Handling: Conveyors are used for various material handling tasks in mining, such as loading and unloading trucks, stockpiling materials, feeding crushers or screens, and transferring materials between processing equipment. 3. Efficiency and Productivity: Conveyors impro...